Overview
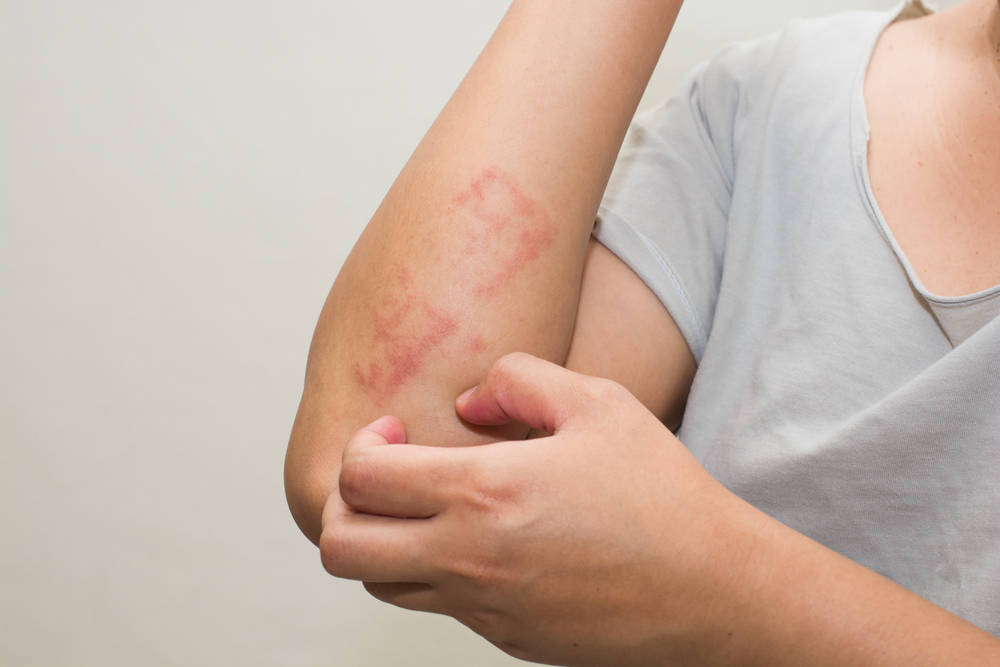
When the immune system reacts to something harmless, causing an allergic reaction is a skin allergy. Different allergens can cause allergies, such as pollen, plants, food, certain medications, etc. Itching, bumps, redness, and other skin conditions are common. Sometimes, their cause may not be easily identifiable. Sometimes, it can be due to medical conditions like chickenpox or measles. An allergist can diagnose the cause of an allergy. There are many preventive methods and treatment options available to treat allergies.
What is Skin Allergy?
Skin allergy is a condition where the immune system reacts to certain harmless substances identifying them as allergens. Skin experiences a reaction when it comes in contact with a particular substance that it is allergic to. Exposure can be by any means direct contact, ingestion, inhalation, or injection. Medically, skin allergies of all kinds are called hypersensitivity reactions. The one that manifests as an immediate reaction is called a Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction, and the one with a delayed onset is called Type 4 hypersensitivity reaction.
What are the Types of Skin Allergies?
There are some types of skin allergies; a few of them include:
- Urticaria or hives
- Atopic dermatitis
- Contact allergic dermatitis
- Angioedema (Swelling)
Urticaria or Hives: Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction caused by antibody IgE (Immunoglobulin E). It can occur due to various antigens that occur internally (e.g., from an infection inside the body) or occur from an external source.
Internal triggers that cause hives include:
- Bacterial infections like upper respiratory tract infections or urinary tract infection
- Infestations such as amoebiasis or giardiasis
- Systemic diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus referred to as SLE (a long-term autoimmune disorder)
External triggers that cause hives include:
- Inhalants – pollen, animal dander, plant hair
- Food – eggs, seafood, meat, and vegetables
- Drugs – penicillin and over-the-counter painkillers
- Physical agents – heat, cold, or injury
Symptoms of Hives
Some of the symptoms of hives include:
- The dermis (the deeper layer of the skin) becomes swollen due to the expansion of blood vessels.
- Lips get swollen
- Itching is common
- May notice respiratory symptoms, such as a runny nose, wheezing, and breathing difficulty along with skin manifestations.
- May notice heaviness in the chest and abdominal pain
Diagnosis of Hives
The physician will ask for a detailed history of the onset, type of symptoms, and duration. Routine tests like blood, urine, and stool examinations are also conducted. Skin tests may also be advised.
Treatment for Hives
Prevention is better than cure — this old adage holds true in the case of hives.
If the allergen is known to you, avoid it at all costs. For example, if artificial jewelry containing nickel triggers allergy, choose your jewelry with care. If you know you are likely to break out due to exposure to the allergen, take an antihistamine (anti-allergic). You can choose an over-the-counter medication containing chlorpheniramine or diphenhydramine.
If a very small area of the skin is affected, a steroid ointment (hydrocortisone) applied locally will help. You could also try calamine lotion as it has a soothing effect on irritated skin.
Cold compresses and ice applications offer a temporary solution. Avoid hot water in the case of hives, as it worsens the condition.
If the cause of hives is stress or emotional turmoil, try a tea brew of peppermint or chamomile to calm the nerves.
Preventive Measures for Hives
Some of the preventive measures for hives include:
- Identify your triggers, such as pet danders, pollen, dust, certain food items, and medications, and avoid them as much as possible.
- Wear loose-fitting outfits made up of cotton.
- Take your medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Soothe your skin by taking baths and applying moisturizer as and when needed.
Atopic Dermatitis: If you have atopic dermatitis, stay away from irritants such as dust, cigarette smoke, woolen, and synthetic fibers.